View sample disease research paper. Browse research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a health research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
Abstract
Disease is a phenomenon that appears to have struck people globally at all times. However, the conceptions of what disease is have varied with time and place. This research paper gives an overview over various conceptions of disease and highlights what is at stake in the debates on the concept of disease. The core questions for the article are: what is disease and what are the ethical issues entangled in this question?
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% OFF with 24START discount code
Introduction
Disease is a phenomenon experienced by most people during their lifetime, and it is something most people fear. Disease is a core concept in the health sciences, in philosophy, and in bioethics, but it is difficult to define. Broadly speaking there are three types of definitions of disease: descriptivist, normativity, and hybrid definitions of disease, claiming that disease is given by phenomena described in nature, by human norms, or both nature and human norms, respectively.
The concept of disease is ethically important as it sets standards and limits, e.g., to what a health-care system is supposed to do and who deserves access to certain goods. It also influences people’s self-conception, their relations to others, their social roles, and their social status. Disease also raises a series of ethical issues, especially related to overdiagnosis and underdiagnosis, undertreatment and overtreatment, medicalization, and just distribution of healthcare resources. This makes disease an important concept with far-reaching implications for individuals, health professionals, health insurers, health policy makers, bioethicists, and politicians.
History And Development
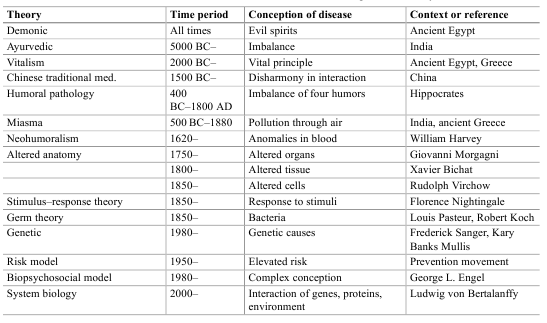
From the interest of understanding and helping people, a wide range of theories and conceptions of disease have emerged. Such theories have altered with time and place. Table 1 gives a brief outline of some theories of disease.
This eagerness to understand disease can make us wonder, why is it so important to understand what disease is? Why is the concept of disease needed? There appear to be many reasons why the concept of disease is important:
- Disease implies a right to attention and care, as disease is related to suffering.
- Disease (in many countries) implies a right to treatment and is thus of great importance to individuals, health professionals, health-care institutions, health insurers, and health policy makers.
- Disease (in many countries) implies exemptions from duties, such as the duty to work or to take care of others (e.g., relatives or friends).
- Disease (in many countries) implies a right to economic compensation (e.g., during sick leave) and therefore is important to individuals, employers, insurers, and health policy makers.
- Disease may exempt from accountability and moral responsibility (in cases of crime).
- Disease is important for individuals to understand their own situation: “I cannot do or be as I would like, because I am diseased.”
- Disease is important for individuals to explain situation to themselves and others.
- Disease has been important to delimit the tasks of health care from other social tasks and topics.
- Disease has been important to classify and organize the tasks of health care, e.g., in taxonomies and hospital departments.
- Disease has been important to delineate the subject matter of health-related sciences.
Table 1. Brief overview of some influential theories of disease throughout the history of medicine
Hence, disease is an important concept with far-reaching implications for individuals, health professionals, health insurers, health policy makers, bioethicists, and politicians. It sets standards, e.g., for how health professionals are educated and how health insurance is regulated, and it sets limits, e.g., who deserves access to certain goods. It also influences people’s self-conception, their relations to others, their social roles, and their social status (see below).
Conceptual Clarification/Definition
There have been many definitions of disease, all trying to highlight or clarify the various important aspects of disease given in the list above (Reznek 1987; Humber and Almeder 1997; Caplan et al. 1981; Cooper 2002; Murphy 2008; Ereshefsky 2009). At present, there is little agreement on how to define disease. The various definitions can be classified in descriptivist, normativist, and hybrid definitions.
Descriptivist positions define disease in terms of biological or mental phenomena which can be described in nature (Davies 2003). Hence, such definitions are often also called naturalist definitions. According to the most referred descriptivist definition, disease is an internal condition disturbing natural functioning. Hence, if a bodily or mental function is reduced below what is statistically normal, then there is disease. This definition is oftentimes called “the biostatistical theory of disease,” and it takes into account differences due to gender, age, and species, so that functional differences in such factors do not become diseases (Boorse 1975). That is, a person is not diseased although the person’s heart has reduced functioning at the age of 100 years old compared to the total population. Diseases are kinds that occur in nature, i.e., natural kinds, and they can be classified on the basis of characteristics that can be described in nature.
According to normativist definitions, disease is a social convention. Disease is the judgment that someone is harmed in a way that (is decided that) can be explained in terms of bodily or mental conditions or processes. Hence, human norms of harm decide what disease is and not biological or mental phenomena, therefore the name normativist. Accordingly, diseases are not natural kinds, although they may be classified according to phenomena which are considered to occur in nature. The reason is that the phenomena that is studied and classified in nature are so classified because they serve human interests, e.g., helping people. The electrical signals in the heart (measured by ECG) are of relevance for medicine because professionals think that they relate to something harmful that can be avoided. When the troponin level in the blood appears to be better in order to characterize, treat, or prevent disease, e.g., myocardial infarction, professionals (and subsequently laypersons) will pay attention to troponin. Correspondingly, it is because blood pressure is related to something harmful that hypertension is of interest in medicine. According to a normativist conception of disease, the phenomena that are measured and manipulated in medicine are relevant to medicine due to human interests (to understand and to help).
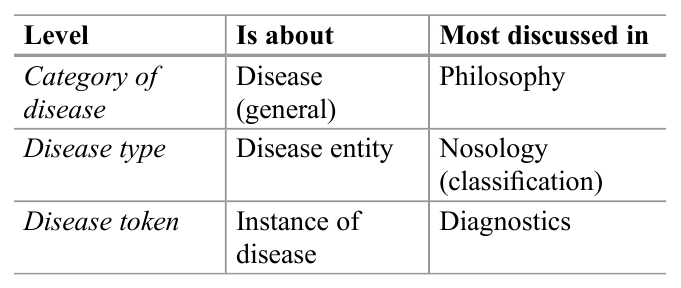
Table 2. Three levels apparent in reflections on disease
Hybrid definitions of disease can be placed between descriptivist and normativist definitions of disease, as they combine elements from both. For example, disease has been defined as harmful dysfunction, where dysfunction is a description of phenomena in nature, while the issue whether it is harmful is a value judgment. Only those deviations from normal functioning that are harmful can be termed disease (Wakefield 1992).
The debates on the concept of disease are sometimes complex and confusing. One reason for this can be that it is not always clear what is discussed, e.g., because the three levels described in Table 2 are confused.
There are also a wide range of terms related to disease, which sometimes are used synonymously, such as malady, illness, sickness, injury, wound, lesion, defect, deformity, disorder, disability, impairment, deficit, etc. (Culver and Gert 1982). This research paper will not address all these terms but will try to clarify the relationship between some of them below, i.e., disease, illness, and sickness.
The Ethical Dimension Of Disease
Inherent in the debates on the concept of disease, there are a series of ethical issues, such as disease’s inherent imperative to help, over diagnosis, overtreatment, medicalization, and justice. These will be briefly discussed in the following.
The Imperative To Help
The most obvious ethical aspect of disease is the imperative to help persons who suffer from disease. The term disease indicates that there is something that may be eased. Hence, disease calls us to help persons who are diseased in the best possible manner, either from duty (deontology), in order to maximize the total well-being (consequentialism); from the character of the professional (virtue ethics); or from the calling in the sufferer’s face (proximity ethics).
Who Decides What Disease Is?
In clinical practice as well in public debates, there are controversies on whether specific conditions count as disease. Previously, drapetomania (slaves running away), homosexuality, and dissidence have been counted as disease. Today it is discussed whether obesity, sorrow, baldness, freckles, and caffeine-induced insomnia count as disease. Specific interest groups may argue that something is a disease, while professionals may be hesitant, or conversely professionals may measure certain biological conditions that are not experienced by persons at all (and may be never will). Correspondingly, society may consider something to be a disease, while persons and professionals disagree. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) may be but one example. Hence, who decides? This is a moral question that relates to the debate between descriptivists and normativists.
Descriptivists tend to claim that nature decides. It is given by nature whether something is a disease or not, i.e., by abnormal functioning of some organ or process. But where to set the limits between normal and pathological? Does nature tell us the limit of glycated hemoglobin (A1C) in the blood for having diabetes type 1? Although hard core descriptivists claim that nature does, critiques argue that such limits are defined from human interests of trying to help people in the best possible manner. If they are right, there are normative aspects at the core of the descriptivists’ conception of disease. Normativists on the other hand are clear that disease is based on human interests and values. However, it is not clear how values and interests are to be balanced. Is it the patients’, the professionals’, relatives, or society’s values and interests that will decide what disease is?
In order to try to clarify some of the conceptual and normative issues, it has been suggested to differentiate between various perspectives of disease, as indicated in Table 3.
Table 3. Characteristics of three perspectives of human ailment: disease, illness, and sickness
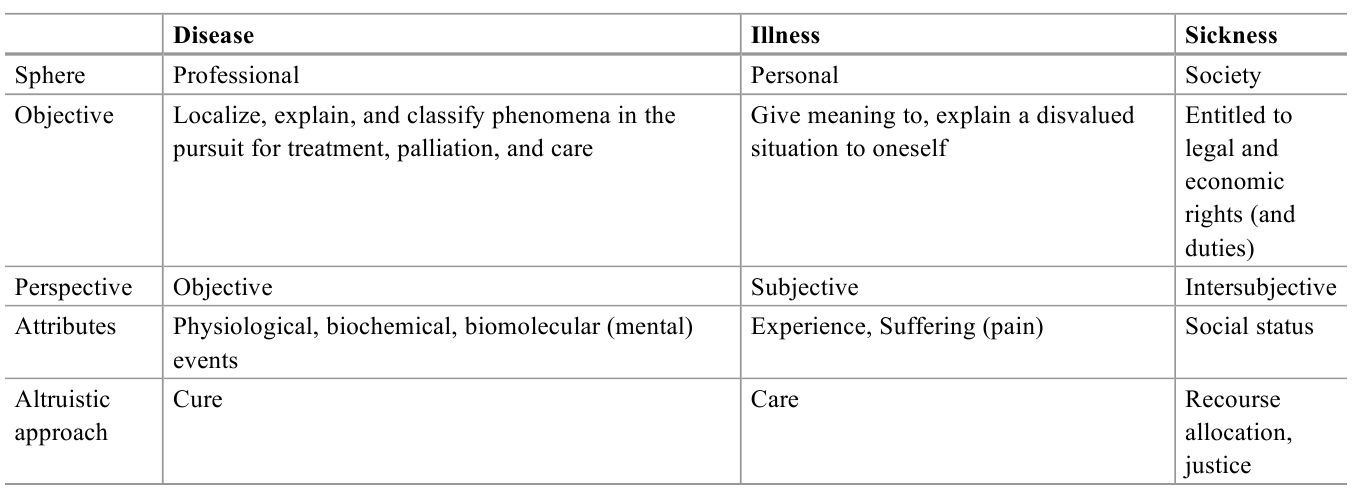
The three perspectives can explain some of the conceptual controversies, as it may be difficult to cover all perspectives of human ailment by one concept. Moreover, the perspectives may also clarify some of the normative issues in terms of conflict of interest between persons, professionals, and society (Hofmann 2002). Impotence (at the age of 70) may not be considered to be a disease from a medical perspective or a sickness from a social perspective, but it definitely may be perceived to be an illness, i.e., it is illness, but not disease and sickness. If all perspectives cohere, there is little controversy. If the perspectives diverge, there may be conceptual and ethical challenges.
Figure 1 indicates the relationship between the concepts of illness, sickness, and disease. Other perspectives, such as existential and risk-related perspectives, may be added.
Figure 1. The relationship between the concepts of illness, sickness, and disease
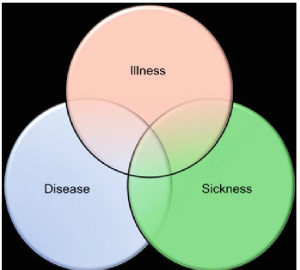
As can be seen from vast and vivid debates on specific diseases, such as obesity, ADHD, and myalgic encephalomyelitis, there is no general agreement on whose perspective is prevailing. While descriptivist definitions of disease will favor the professional perspective, normativist definitions will have a higher affinity to social perspectives. Several positions in bioethics will favor the personal perspective on human ailment, i.e., illness (Toombs 1990; Carel 2008).
Underdiagnosis And Overdiagnosis, Undertreatment And Overtreatment
The concept of disease delimits diseased from non-diseased, and where this limit is set is of ethical significance. If the limit is set so that suffering persons who could have been helped are excluded, this is morally wrong. They are underdiagnosed, may be undertreated, and may experience unnecessary uncertainty, anxiety, pain, and death. Conversely, if the limits are too low, it is morally wrong as well. Then healthy persons are diagnosed as having a disease. They may become anxious from being diagnosed and they may be treated unnecessarily and have side effects from unnecessary treatment. While underdiagnosed persons oftentimes gain attention in the media (“could have been saved”), over diagnosed persons get little attention. They do not know that they are over diagnosed but are actually happy that “they found something and saved my life.” Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) may be one example, as it can result in invasive breast cancers, but it does not always do so. When found, DCIS are oftentimes treated as breast cancer, although one does not know whether they would actually have caused symptoms, suffering, or death.
Making Risk A Disease
Another ethical issue related to the concept of disease is the predictive aspirations in modern medicine. A wide range of tests are able to predict diseases. The ethical drive for this is to detect disease before it becomes noticeable and, by prevention or early treatment, to avoid disease or diminish its consequences. However, very few tests are perfect. The outcomes of tests are uncertain and so are the outcomes of subsequent treatment. Hence, the test provides a risk, or a range of risks, for a certain disease. For example, 55–65 % of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation will develop breast cancer by age 70 years, while about 12 % of women in the general population will develop breast cancer sometime during their lives. Hence, testing positive for the BRCA1 mutation significantly increases the risk of breast cancer but does not mean that the person will have breast cancer. It is a risk estimate. Such risk estimates do not only give people important opportunities to save their lives and reduce suffering; it also gives them difficult choices, as it is uncertain whether they will become diseased, e.g., should a woman prophylactically remove her breasts? Hence, handling risk factors as disease poses ethical challenges to health policy makers, health professionals, and, last but not least, to individual persons. This also connects to ethical challenges with the right to know and the right not to know. The issue of making risk a disease relates to another ethical issue in modern medicine: medicalization.
Medicalization
It has been widely argued that the conception of disease has become too wide and inclusive, e.g., that it has come to include conditions that are considered to be part of ordinary life, such as sorrow (Horwitz and Wakefield 2007), stress, unhappiness, and various kinds of social behavior. It may be ethically challenging when the conceptions of disease make ordinary life conditions or behaviors subject to medical attention. Hence, the critique of medicalization is closely connected to the (unreflective) expansion of the concept of disease.
Disease As An Existential Threat
As disease traditionally has been life threatening and because most people die from a disease, disease is an existential issue. Hence, getting the message of having a disease may be disturbing and challenging, meriting attention and care, beyond handling the disease. Moreover, some diseases have symbolic attributes. Cancer has been considered to be a death sentence and has been a stigma. While the existential aspects of disease have been were at the core in the hospital tradition and still are in many parts of the world, they have gained less attention in modern Western medicine.
Social Prestige And Stigma
Disease is normally considered to be something negative. However, it may also have some positive aspects, such as increased attention, right to treatment, economic compensation, and freedom from duties (work), as pointed out before. Specific disease labels may give identity and strong relations between persons with the same disease. Conversely, not being labeled diseased may make people feel deserted, in despair, and guilty. Hence, disease labeling may influence people’s self-conception and self-esteem.
Moreover, professionals appear to have a relatively stable prestige hierarchy for disease entities (Album and Westin 2008). Organ specific diseases have higher prestige than vague diseases. Diseases related to organs placed in the upper part of the body, such as brain and heart, have higher prestige than those related to organs in lower body parts. Acute diseases prevail over chronic diseases. Hi-tech diseases trump low-tech or no-tech diseases. Such prestige hierarchies of disease tend also to be present in laypeople and patients as well. When disease hierarchies influence how patients are handled or how resources are allocated or prioritized, it becomes ethically challenging.
Justice
Conceptions of disease also raise ethical concerns beyond prestige hierarchies. The 90–10 gap is ethically relevant, as 90 % of research resources go to diseases relevant for 10 % of the global population. Correspondingly, it may also be argued that the disease concepts used in the economically richer part of the world is of little relevance to the poorer part of the world. It appears to be ethically important to increase the attention to disease entities that prevail in poorer populations, as well as avoiding a general disease concept that is biased toward affluent populations.
Conclusion
Disease is a phenomenon experienced by most people during life. It is something most people fear, and it is a core concept in the health sciences, in philosophy, and in bioethics. Descriptivists tend to define disease as the malfunctioning of some organ or process and argue that diseases are natural kinds. Normativists, on the other hand, argue that disease is not discovered in nature but is the judgment that someone is harmed in a way that can be explained in terms of bodily or mental conditions or processes. Hybrid conceptions of disease claim that disease is both descriptive and normative, e.g., as harmful dysfunction.
The concept of disease sets standards and limits, e.g., to what a health-care system is supposed to do and who deserves access to certain goods. It also influences people’s self-conception, their relations to others, their social roles, and their social status. Hence, disease is an important concept with far-reaching implications for individuals, health professionals, health insurers, health policy makers, bioethicists, and politicians. It also raises a series of ethical issues, especially related to over diagnosis and underdiagnoses, under treatment and overtreatment, medicalization, and just distribution of health-care resources.
Bibliography :
- Album, D., & Westin, S. (2008). Do diseases have a prestige hierarchy? A survey among physicians and medical students. Social Science and Medicine, 66(1), 182–188.
- Boorse, C. (1975). On the distinction between disease and illness. Philosophy and Public Affairs, 5, 49–68.
- Caplan, A., Englehardt, H., Jr., & McCartney, J. (Eds.). (1981). Concepts of health and disease: Interdisciplinary perspectives. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Carel, H. (2008). Illness: The cry of the flesh. Dublin: Acumen.
- Cooper, R. (2002). Disease. Studies in the History and Philosophy of Biology & the Biomedical Sciences, 33, 263–282.
- Culver, C. M., & Gert, B. (1982). Philosophy in medicine. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Davies, P. S. (2003). Norms of nature. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Ereshefsky, M. (2009). Defining ‘health’ and ‘disease’. Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences, 40(3), 221–227.
- Hofmann, B. (2002). On the triad disease, illness and sickness. Journal of Medicine and Philosophy, 27(6), 651–674.
- Horwitz, A. V., & Wakefield, J. C. (2007). The loss of sadness. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Humber, J. M., & Almeder, R. F. (Eds.). (1997). What is disease? Totowa, NJ: Humana Press.
- Murphy, D. (2008). Health and disease. In A. Plutynski & S. Sarkar (Eds.), The blackwell companion to the philosophy of biology (pp. 287–298). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
- Reznek, L. (1987). The nature of disease. New York: Routledge.
- Toombs, K. (1990). The meaning of illness: A phenomenological account of the different perspectives of physician and patient. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
- Wakefield, J. (1992). The concept of mental disorder: On the boundary between biological facts and social values. American Psychologist, 47, 373–388.
- Mukherjee, S. (2011). The emperor of all maladies. A biography of cancer. New York: Scribner.
- Sigerist, H. A. (1961). History of Medicine. Vol. II: Early Greek, Hindu, and Persian Medicine. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Sontag, S. (1978). Illness as metaphor. New York: Farrar. Strays and Giroux.
- Taylor, F. K. (1979). The concepts of illness, disease and morbus. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.




